Side Effects: What to Watch For and How to Handle Them
Side effects are the common reason people stop a medicine or call their doctor. Some are mild and short-lived, like stomach upset after antibiotics. Others are serious and need fast action, like trouble breathing or sudden swelling. This page collects practical guides and real tips so you can spot problems, reduce risk, and find safer options when needed.
Common side effects to expect
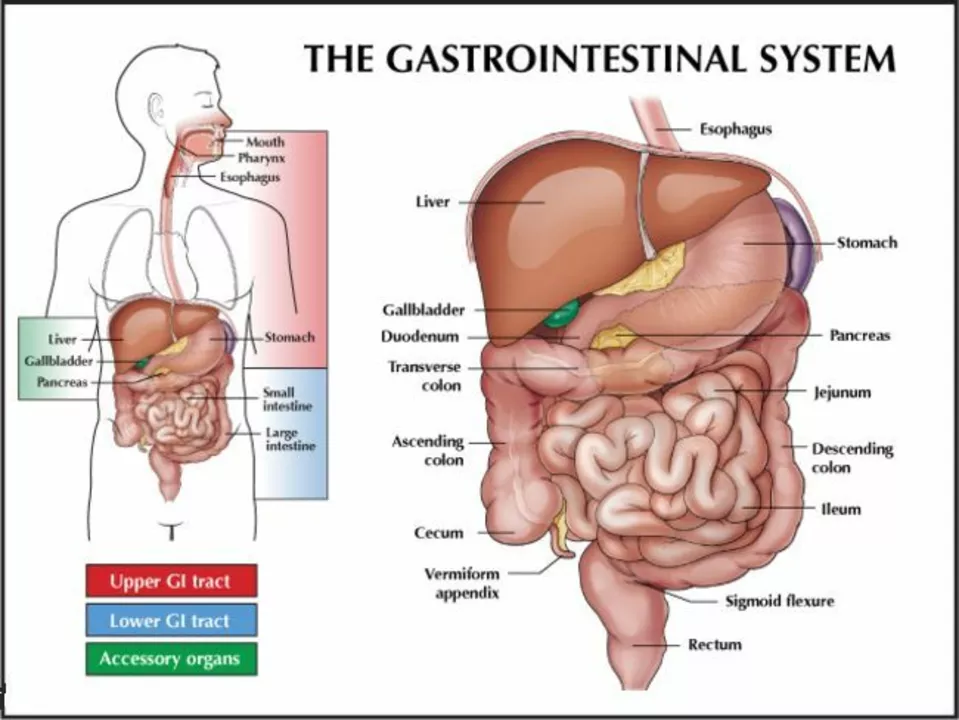
Knowing the typical reactions helps you react calmly. For many antibiotics you might see nausea, diarrhea, or yeast infections. Statins and cholesterol combos can cause muscle aches or mild digestive issues. ADHD medicines like atomoxetine may bring sleep changes, reduced appetite, or mood shifts. Diuretics such as furosemide commonly cause increased urination, dizziness, or low potassium. These are examples — read your medicine leaflet for specifics.
Watch for red flags that need immediate care: severe rash, swelling of face or throat, trouble breathing, fainting, chest pain, sudden severe headache, or new suicidal thoughts. If any of those occur, get urgent medical help.
Quick steps if you suspect a side effect
1) Stop, but don’t panic. If the reaction is mild, pause the medication only after checking with a pharmacist or doctor. For severe signs, stop and seek emergency care. 2) Keep a simple record: drug name, dose, when the symptom started, and what you did. That helps your clinician decide fast. 3) Check interactions. Some side effects come from drug combinations — mention all prescriptions, OTC meds, and supplements. 4) Ask about alternatives. Many posts here compare substitutes (for example statin swaps or antibiotic options) so you can discuss real alternatives with your prescriber.
If a medicine causes side effects that reduce quality of life, it’s fine to ask for a different option. Alternatives may have different side-effect profiles, dosing schedules, or monitoring needs. For example, if a diuretic makes you dizzy, your doctor might try a different class or adjust the dose.
Buying meds online? Safety matters when shopping for prescriptions. Always use reputable pharmacies, confirm prescriptions, and avoid offers that sound too cheap or require no prescription for prescription-only drugs. Several guides on this site explain how to judge online pharmacies and stay legal and safe.
Reporting side effects helps others. Tell your doctor and consider reporting serious or unexpected reactions to your country’s medicine regulator. That feedback improves safety data for everyone.
Use this tag to find focused articles on drug reactions, comparisons of alternatives, real-world tips for managing symptoms, and safe online pharmacy advice. If you want help reading a leaflet or deciding whether to call your doctor, open a relevant article or search by the specific medicine name — you'll get clear, practical steps to take next.