The Importance of Understanding Azelastine's Effects on the Gastrointestinal System
As a widely used antihistamine, Azelastine has proven to be an essential medication for many people suffering from allergies, hay fever, and other respiratory issues. However, like all medications, it is vital for us to understand how it may affect other parts of our body, particularly the gastrointestinal (GI) system. In this article, I will discuss the impact of Azelastine on the gastrointestinal system, breaking down the information into six key sections.
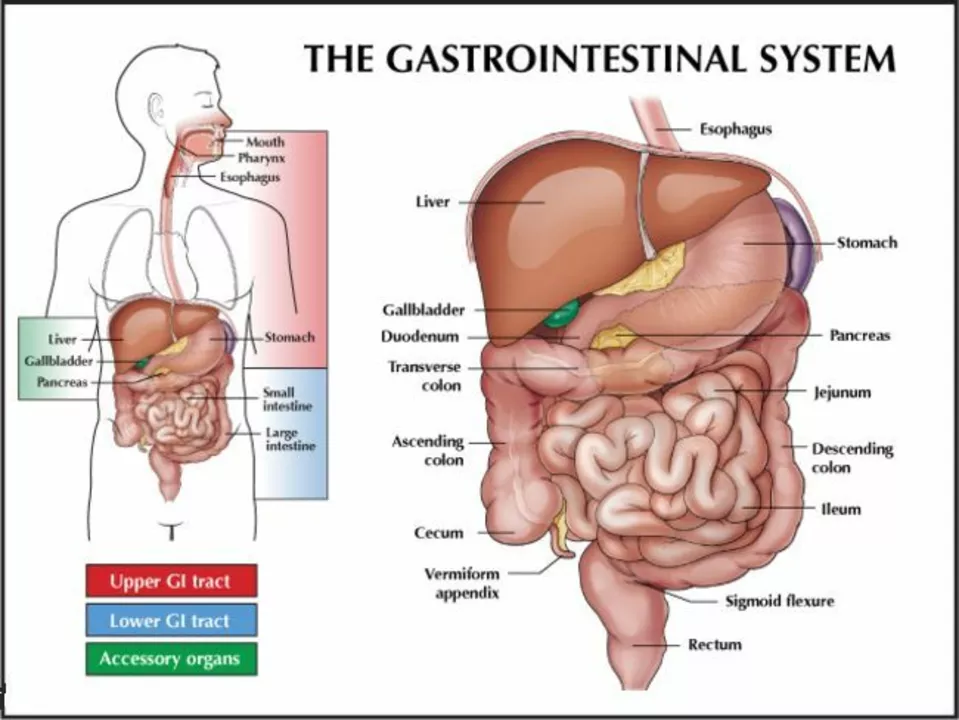
How Azelastine Works and its Connection to the Gastrointestinal System
Azelastine is an antihistamine, which means it works by blocking the action of histamines – substances responsible for causing allergy symptoms such as sneezing, itching, and nasal congestion. While its primary function is related to the respiratory system, it is crucial to recognize that the gastrointestinal system can also be affected by histamines. Histamines play a role in regulating stomach acid secretion, intestinal motility, and inflammation in the GI tract. Therefore, it is important to consider how blocking histamines with Azelastine may impact the gastrointestinal system.
Digestive Symptoms and Side Effects of Azelastine
While Azelastine is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience side effects related to the gastrointestinal system. Common digestive symptoms that have been reported include nausea, dry mouth, and dyspepsia (indigestion). These side effects are generally mild and temporary, but it is essential to be aware of them, especially if you are starting Azelastine treatment or increasing your dosage. If you experience severe or persistent digestive symptoms, consult your healthcare provider for guidance.
The Role of Azelastine in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic condition in which stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. Histamines are known to stimulate the production of stomach acid, which can exacerbate GERD symptoms. As an antihistamine, Azelastine may potentially have a positive impact on GERD by reducing histamine-induced acid secretion. However, more research is needed to establish a definitive link between Azelastine and GERD treatment.
Azelastine and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits. The exact cause of IBS is still unclear, but it is believed that an imbalance of chemicals in the gut, including histamines, may contribute to the condition. Some studies have suggested that antihistamines like Azelastine could potentially help alleviate IBS symptoms by blocking the action of histamines in the gut. However, further research is required to confirm the efficacy of Azelastine in treating IBS.
Drug Interactions and the Gastrointestinal System
It is important to consider possible drug interactions when taking any medication, including Azelastine. Certain medications may increase the risk of gastrointestinal side effects or alter the way Azelastine is metabolized in the body. For example, some antacids and acid-reducing medications may interfere with the absorption of Azelastine, potentially reducing its effectiveness. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new medications and inform them of all the medications and supplements you are currently taking.
Conclusion: The Importance of Monitoring and Communicating with Your Healthcare Provider
In conclusion, while Azelastine is an effective treatment for allergy symptoms, it is essential to be aware of its potential impact on the gastrointestinal system. Although side effects are generally mild and temporary, always consult your healthcare provider if you experience severe or persistent digestive symptoms. Additionally, it is vital to discuss any potential drug interactions and keep your healthcare provider informed of all medications and supplements you are taking. By staying informed and vigilant, you can ensure the safest and most effective treatment for your allergy symptoms.
Nic Floyd
April 28, 2023 AT 00:39
Yo folks, azelastine is a H1 blocker that can tweak your gut micro‑environment 🚀 It’s not just sneezes it touches histamine‑mediated acid pumps 🤓 When you stack it with antacids you might see a dip in absorption so keep an eye on the dosage 🙌 Also, watch out for mild nausea or dyspepsia, those are usually transient 😅 If you’re on a polypharmacy regimen, run a quick med‑check 📋
Johnae Council
April 29, 2023 AT 22:26
Ugh, another post trying to sound scientific while we’re just trying not to feel like a balloon every time we take our allergy meds.
Manoj Kumar
May 1, 2023 AT 16:06
Ah, the grand tapestry of histamine pathways, where a nasal spray can whisper sweet nothings to the stomach lining. It is almost poetic, if one pretends that the gut isn’t a chaotic bazaar of microbes debating the meaning of existence. Azelastine, that diligent sentinel, blocks histamine receptors, yet in doing so, it may inadvertently mute the subtle signals that guide gastric acid production. One could argue that this is a benevolent side‑effect for the GERD‑afflicted, as less acid means less erosion, but the gut is not a monolith; it is a symphony of cells each playing a part. The reduction of histamine may also temper the motility of the intestines, perhaps offering a fleeting reprieve for those plagued by IBS’s endless loops of cramping and bloating. However, such benefits are speculative at best, and the literature remains a patchwork of small studies and anecdotal whispers. In the meantime, the patient is left juggling the promise of relief against the specter of nausea, dry mouth, and the ever‑present dread of drug interactions. Should we, as humble observers, not also consider the psychosomatic dimension? The mind, after all, interprets the rumble of the stomach through the lens of expectation. If one expects severe side‑effects, the gut may oblige with a chorus of complaints. Conversely, a calm outlook might soften the impact, turning a potential adverse event into a trivial footnote. So, perhaps the true impact of azelastine on the gastrointestinal system lies not solely in pharmacology, but also in the narrative we construct around it. Regardless, physicians must remain vigilant, prompting patients to report any lingering discomfort, no matter how minor. The dialogue between prescriber and patient becomes the safety net catching those rare but real complications. In short, azelastine’s role in the gut is a nuanced dance-sometimes a gentle waltz, other times a stumbling tango, but always deserving of a closer look.
Hershel Lilly
May 3, 2023 AT 09:46
I’ve noticed that when I start azelastine, my stomach settles after a day or two. It’s subtle, but worth monitoring if you have a sensitive gut.
Carla Smalls
May 5, 2023 AT 03:26
Just a friendly heads‑up: if you experience persistent nausea, don’t ignore it. Talk to your doctor early so they can adjust the dose or suggest an alternative.
Monika Pardon
May 6, 2023 AT 21:06
Esteemed colleagues, it is with a modicum of scepticism that I posit the notion that azelastine’s purported gastrointestinal benefits are perhaps a grand fabrication orchestrated by pharmaceutical interests. One must, however, also acknowledge the anecdotal reports circulating amongst the lay populace, which, while lacking rigorous validation, hint at a marginal amelioration of reflux symptoms. Nonetheless, I caution against precipitous adoption of such claims without robust, peer‑reviewed evidence.
Rhea Lesandra
May 8, 2023 AT 14:46
Let’s keep this conversation constructive! Azelastine can be a useful tool, but remember to stay hydrated and eat small, balanced meals to support your gut while you’re on the medication. Small steps make a big difference.
Kasey Marshall
May 10, 2023 AT 08:26
Good point, Rhea. I’ve found that taking azelastine with food reduces the dry‑mouth sensation for me.
Dave Sykes
May 29, 2023 AT 00:39
Stay proactive: keep a symptom diary and share it with your healthcare provider to fine‑tune your treatment plan.