Eye Pressure Medication: A Practical Overview
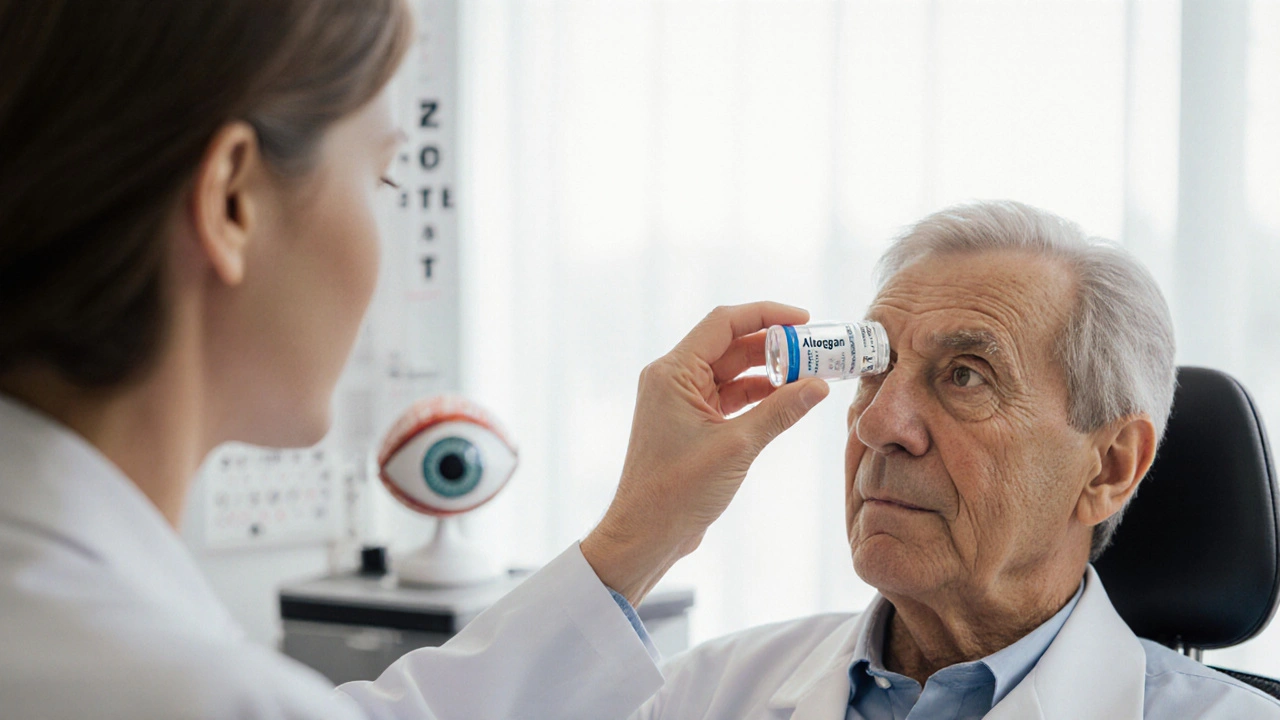
When dealing with Eye Pressure Medication, drugs used to lower intra‑ocular pressure (IOP) and protect the optic nerve. Also known as IOP‑lowering drugs, it plays a crucial role in managing Glaucoma, a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, often because of high pressure inside the eye. In simple terms, if you think of the eye as a balloon, eye pressure medication is the valve that prevents the balloon from over‑inflating and cracking. This introductory guide breaks down the major drug families, explains how they work, and points out what to watch for when you or a loved one starts treatment.
Key Drug Classes for Lowering Eye Pressure
Most prescriptions fall into a handful of well‑studied classes. Prostaglandin analogs, the most commonly prescribed first‑line drugs, increase fluid outflow through the eye’s drainage pathways and usually require just one drop a day. Beta blocker eye drops, reduce aqueous humor production by blocking adrenaline receptors in the ciliary body are another popular option, especially for patients who can’t tolerate prostaglandins. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, work by decreasing the enzyme that helps produce fluid inside the eye often serve as add‑on therapy when a single drug isn’t enough. Alpha‑agonists, rho‑kinase inhibitors, and combination drops blend two mechanisms in one bottle, giving doctors flexibility to hit the target pressure without stacking multiple bottles.
Choosing the right regimen isn’t just about lowering numbers on a chart; it’s also about lifestyle, side‑effects, and how well a patient can stick to the schedule. Prostaglandins can cause darkening of the iris or extra eyelashes, while beta blockers may affect heart rate or trigger cold hands. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors sometimes lead to a metallic taste or mild stomach upset. Doctors often start with the safest, most effective option (usually a prostaglandin) and adjust based on response and tolerance. For stubborn cases, laser therapy or minimally invasive surgery may be recommended, but medication remains the backbone of long‑term control. Below you’ll find a collection of articles that dive deeper into each drug class, compare prices, explain how to buy them safely online, and offer tips on staying on track with your eye‑health routine.