Antithyroid Medication: What It Is, How It Works, and What You Need to Know
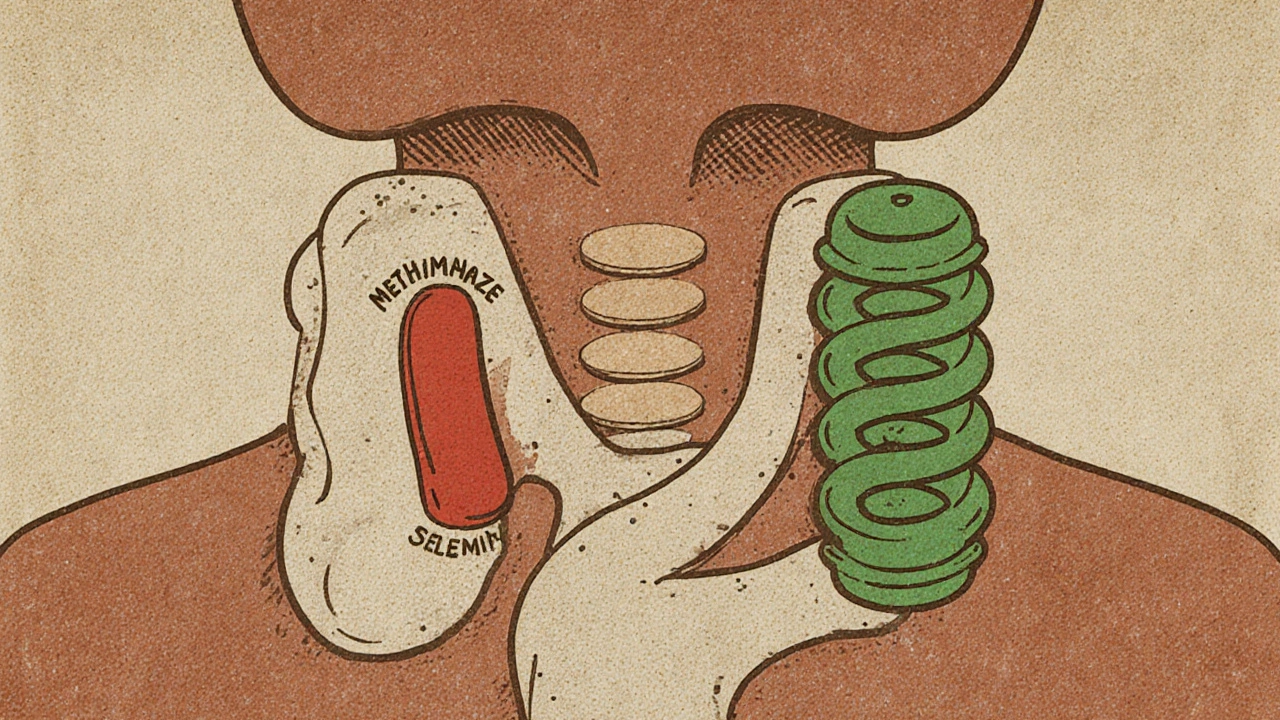
When your thyroid goes into overdrive, antithyroid medication, a class of drugs designed to reduce excess thyroid hormone production. Also known as thyroid suppressants, these drugs are often the first line of defense for conditions like Graves’ disease or toxic nodules. They don’t cure the root cause, but they bring hormone levels back to normal so your body can catch up—without surgery or radiation. Unlike levothyroxine, a synthetic thyroid hormone used to replace what the body lacks, antithyroid medication actually slows down the gland’s output. That’s a key difference: one replaces, the other restrains.
Common antithyroid drugs include methimazole and propylthiouracil. Methimazole is usually preferred because it works longer and has fewer side effects, though both can cause rashes, joint pain, or, rarely, liver issues. If you’re on one of these, your doctor will check your blood regularly—not just for thyroid levels, but for white blood cell counts. A drop in those can signal a serious reaction. You also need to know how these drugs interact with others. For example, taking them with protein shakes, a popular supplement often used for muscle building right after your dose can interfere with absorption, just like with levothyroxine. Timing matters. Most doctors recommend taking antithyroid meds on an empty stomach, at least an hour before food or supplements.
People often wonder if antithyroid medication is permanent. For some, it’s a bridge—used for 12 to 18 months, then stopped to see if the thyroid settles down. For others, it’s long-term, especially if the condition keeps coming back. It’s not the only option, but it’s the most common non-surgical approach. You’ll also see it mentioned alongside other thyroid-related topics: drug safety, pill splitting for cost savings, and how food affects absorption. These aren’t random connections. They’re real-life concerns for anyone managing thyroid health. Whether you’re just starting treatment or have been on it for years, understanding how these drugs behave in your body helps you avoid mistakes, reduce side effects, and stay in control.
Below, you’ll find practical guides on how to manage your meds safely—whether you’re splitting pills to save money, timing your doses around meals, or checking for hidden interactions with other drugs. These aren’t theoretical tips. They’re based on real patient experiences and clinical guidance, pulled straight from posts that help people actually use their medications better.