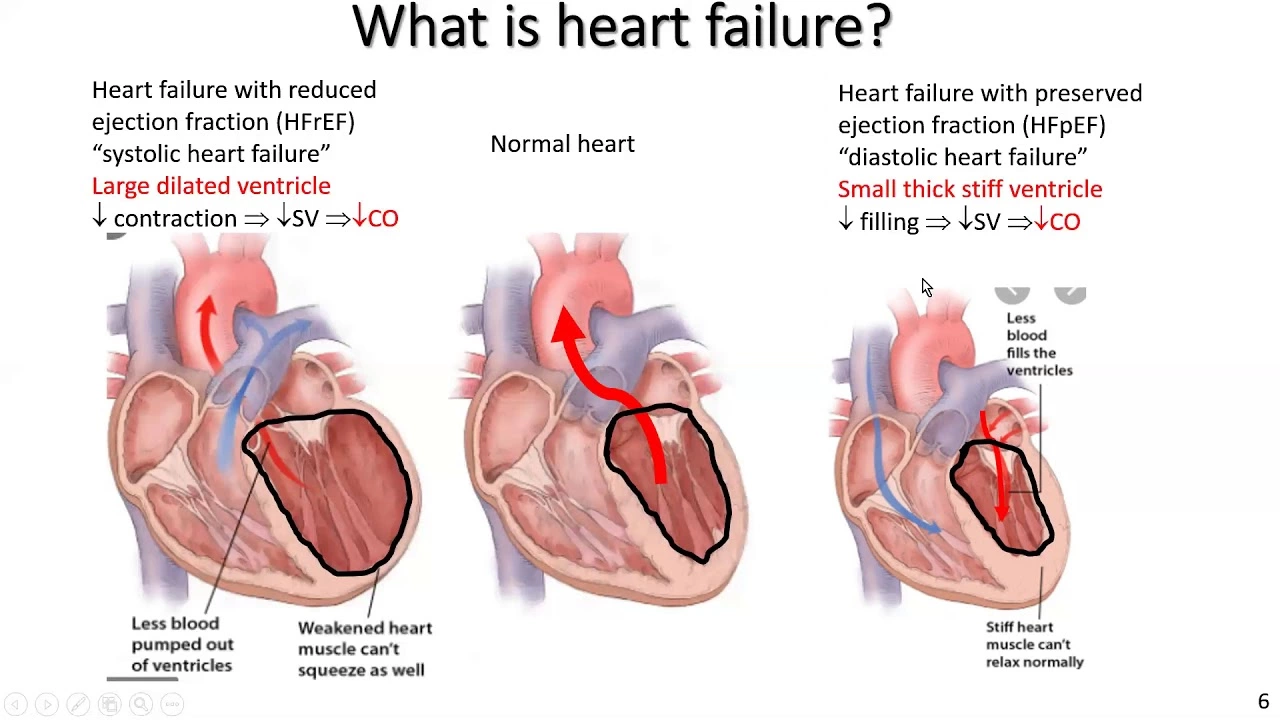
Understanding Chronic Heart Failure
Before diving into the effects of alcohol and smoking on chronic heart failure, it's important to understand what chronic heart failure is. Chronic heart failure, also known as congestive heart failure, is a condition where the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently. When this occurs, the body struggles to maintain a balance between oxygen and nutrients, which can lead to a number of health complications. Symptoms of chronic heart failure include shortness of breath, fatigue, and fluid retention. In this article, we will explore the impact of two common lifestyle factors - alcohol consumption and smoking - on this condition.
The Role of Alcohol in Chronic Heart Failure
Alcohol can have a significant impact on the development and progression of chronic heart failure. Moderate alcohol consumption is generally considered safe for most people, but excessive or binge drinking can lead to a number of health problems, including heart failure. Drinking large amounts of alcohol can weaken and damage the heart muscle, making it less able to pump blood efficiently. This condition, called alcoholic cardiomyopathy, can eventually lead to chronic heart failure.
Additionally, alcohol can increase blood pressure and contribute to the development of heart disease, both of which are risk factors for chronic heart failure. It's important to note that alcohol affects everyone differently, and some people may be more susceptible to its harmful effects on the heart than others. If you have a history of heart problems or are at risk for developing chronic heart failure, it's best to talk to your doctor about the safest level of alcohol consumption for you.
Smoking and Its Effects on Chronic Heart Failure
Smoking is a well-known risk factor for a variety of health complications, including chronic heart failure. The chemicals in cigarette smoke can damage the heart and blood vessels, leading to atherosclerosis (the buildup of plaque in the arteries). This can cause the arteries to narrow and harden, increasing the risk of heart attack and heart failure. Smoking can also raise blood pressure and heart rate, putting additional strain on an already weakened heart.
Moreover, smoking has a negative impact on lung function, which can exacerbate symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath and fatigue. The good news is that quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of developing chronic heart failure and improve overall heart health. If you're a smoker, talking to your doctor about quitting is one of the best things you can do for your heart.
Managing Alcohol and Smoking in Chronic Heart Failure Patients
For those already diagnosed with chronic heart failure, managing alcohol consumption and quitting smoking are crucial steps in managing the condition. Reducing alcohol intake can help prevent further damage to the heart and may even improve heart function. It's important for patients to work closely with their healthcare team to determine the appropriate level of alcohol consumption for their individual situation.
Quitting smoking is another essential step in managing chronic heart failure. Patients who quit smoking experience improvements in lung function and a reduced risk of further heart damage. Quitting smoking can be difficult, but with the support of healthcare professionals and smoking cessation aids, many patients can successfully quit and significantly improve their heart health.
Lifestyle Changes for a Healthier Heart
In addition to managing alcohol consumption and quitting smoking, there are other lifestyle changes that can help improve heart health and reduce the risk of chronic heart failure. These include maintaining a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and managing stress. A heart-healthy diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. Regular exercise can help strengthen the heart muscle, improve circulation, and lower blood pressure. Finally, managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help reduce the strain on the heart and decrease the risk of heart failure.
Medications and Treatment Options for Chronic Heart Failure
While lifestyle changes are crucial in managing chronic heart failure, medications and other treatments may also be necessary. Common medications used to treat heart failure include ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and diuretics. These medications work to reduce the workload on the heart, lower blood pressure, and remove excess fluid from the body. In some cases, more advanced treatments, such as implantable devices or heart transplant surgery, may be necessary to manage chronic heart failure.
It's important for patients with chronic heart failure to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both lifestyle factors and medical treatments. By taking an active role in their own care, patients can significantly improve their quality of life and overall heart health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, alcohol and smoking are two lifestyle factors that can significantly impact the development and progression of chronic heart failure. By managing alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and making other healthy lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce their risk of heart failure and improve their overall heart health. If you or a loved one is struggling with chronic heart failure, it's important to work closely with your healthcare team to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both lifestyle factors and medical treatments.
Jacqui Bryant
June 1, 2023 AT 11:33
Take it one step at a time, you’ve got this!
Lori Brown
June 1, 2023 AT 13:46
Great rundown on how booze and cigarettes hit the heart hard :) It’s crucial to remember that even moderate drinkers should keep an eye on their intake, especially if they have heart issues. Cutting back isn’t just about avoiding damage, it’s about giving your heart a chance to recover and get stronger. If you’re thinking about quitting smoking, lean on support groups or nicotine replacement – they really make a difference. Stay proactive and keep that heart health top of mind – you’re doing the right thing! :)
Paul Luxford
June 1, 2023 AT 15:10
I appreciate the practical advice, especially the emphasis on moderation and seeking support. It’s helpful to frame these lifestyle changes as collaborative efforts with healthcare providers. Maintaining balance while respecting personal limits can foster sustainable habits. Thanks for the balanced perspective.
Nic Floyd
June 29, 2023 AT 02:53
Alcoholic cardiomyopathy represents a reversible form of myocardial dysfunction when the etiologic agent is removed 😊 The pathophysiology involves ethanol‑induced oxidative stress leading to sarcolemmal injury and impaired calcium handling The dose‑response relationship is non‑linear and binge episodes precipitate acute decompensation The renin‑angiotensin‑aldosterone system becomes hyperactive contributing to ventricular remodeling Chronic smokers exhibit endothelial dysfunction mediated by nicotine‑derived nitrosamines which accelerates atherosclerotic plaque formation Smoking also raises catecholamine levels increasing myocardial oxygen consumption The synergistic effect of alcohol and tobacco magnifies afterload and reduces preload efficiency In clinical practice, monitoring biomarkers such as NT‑proBNP can guide therapeutic adjustments The guideline‑directed medical therapy (GDMT) remains cornerstone, yet lifestyle modification augments pharmacologic benefits Patient education should incorporate harm reduction principles rather than abstinence‑only rhetoric to enhance adherence The role of community health workers in smoking cessation has demonstrated cost‑effectiveness and improved quit rates The integration of cardiac rehabilitation programs facilitates supervised exercise, dietary counseling, and psychosocial support The evidence suggests that even modest reductions in alcohol intake can improve ejection fraction over a six‑month horizon The use of nicotine replacement therapy should be tailored to comorbid conditions to avoid precipitating arrhythmias The data also highlight that secondhand smoke exposure can exacerbate heart failure symptoms in vulnerable populations Hence, multidisciplinary teams must address both substance use behaviors and medical optimization The ultimate goal is to prolong survival while preserving quality of life 😊
Johnae Council
June 29, 2023 AT 05:40
Wow, look at that jargon‑fest, almost like a medical textbook on steroids. Sure, all those fancy terms sound impressive, but at the end of the day, it’s still just about cutting back on booze and quitting smokes. No need for a PhD to get that message, plain and simple works best. Let’s keep it real, not a lecture.